It's here. Intel's first smartphone SoC that you'll actually be able to buy in a device before the end of the year. The platform is called Medfield and Paul Otellini just announced its first device partners.
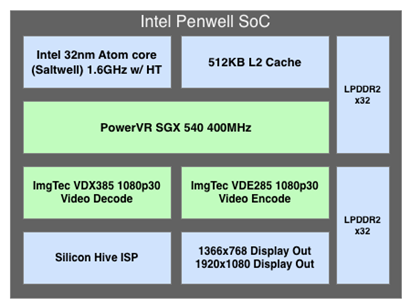
Medfield starts out as a bonafide mobile SoC. Whereas Moorestown was a "two-chip" solution, Medfield is just one - the Penwell SoC:
The SoC is only available in a PoP (Package on Package) configuration measuring 12mm x 12mm. Intel wouldn't give out a die size but it did show me a Penwell sample without the stacked DRAM:
Since I know the measurements of the package I could estimate the dimensions of the silicon itself. My math worked out to be around 62mm^2. That's larger than a Tegra 2-class SoC, but smaller than Tegra 3 or Apple's A5. The diagram of its high level architecture above helps explain why.
There's only a single version of Medfield being announced today: the Intel Atom Z2460. The Z2460 features a single Atom core with a 512KB L2 cache, a PowerVR SGX 540 GPU and a dual-channel LPDDR2 memory interface. In a world where talking about four Cortex A9s and PowerVR SGX 544MP2s isn't uncommon, Medfield starts out almost sounding a bit...tame. But then you see its performance:
Although running what appears to be a stock Gingerbread browser, Intel's Medfield reference platform posts SunSpider performance better than any other smartphone we've tested - including the Galaxy Nexus running Ice Cream Sandwich. Intel promises that Medfield's performance will scale on ICS as well - the gap should be maintained. We've seen high results from reference designs in the past, but the Medfield platform is a little different as you'll soon see - it's a complete smartphone design that should be representative of handsets that hit the market later this year.
Medfield isn't a one trick pony either, performance is similarly dominating under BrowserMark:
These are tablet-like scores. Here the Galaxy Nexus running ICS comes close, but once again Intel expects that on the same OS Medfield should be faster than any of the currently available SoCs.
I asked Intel where its SunSpider and BrowserMark performance advantages came from, especially considering we've typically only seen huge gains with new browsers and not new SoCs. Their response pointed to a bunch of factors, but one stand out issue was the A9 has a great execution core but seems to be more limited on the memory interface. Atom can support far more outstanding misses in L2 than the Cortex A9, which chokes bandwidth to the processor for anything not already in the L2 cache. This may be one of the reasons why we've never been able to get really high bandwidth numbers out of A9 based SoCs. It's probably safe to assume that things will be different with the Cortex A15, but for now it's little things like this that give Medfield a performance advantage.
GPU performance is understandably not as impressive. I couldn't get offscreen numbers of GLBenchmark 2.1 but I did get results at the device's native resolution (1024 x 600):
3D performance is better than the OMAP 4460 due to Medfield's 400MHz GPU clock compared to ~300MHz in most OMAP4 devices.
Performance without power considerations is meaningless, especially in the smartphone world. Luckily for Intel, Medfield seems very competitive there as well. Remember this slide?
Now I've got names and numbers to put to it. The HTC Sensation, Motorola Droid 3, iPhone 4S, LG Optimus 2X and Samsung Galaxy S 2 are all featured in the graphs above. Medfield, at least in Intel's reference platform, looks very good.
The actual values are pretty astonishing as well. Sub 20mW idle, sub 750mW during a call on 3G and although not pictured here, Intel's internal data suggests ~1W power consumption while browsing the web compared to ~1.3W on the iPhone 4S and Galaxy S 2. I've done my own measurements on 4S web browsing and came up with a very similar value.
| Intel Measured Smartphone Power Consumption (Identical Display Brightness) | ||||||
| Standby (3G) | Talk (3G) | Browsing (3G) | Video Playback 720p | |||
| Apple iPhone 4S | ~38mW | ~800mW | ~1.3W | ~500mW | ||
| Intel Medfield Reference | ~18mW | ~700mW | ~1.0W | ~850mW | ||
| Samsung Galaxy S II | ~19mW | ~675mW | ~1.2W | ~650mW | ||
The performance and power data both look great for Medfield. You would think that this data, assuming there's nothing fundamentally wrong, would be enough to convince a handset maker to actually give Intel a shot. You'd be right.
In addition to disclosing Medfield performance data, Intel is also announcing partnerships with both Motorola and Lenovo. The former is a broad, multi-year agreement stating that Motorola plans on creating many devices based on Intel silicon - the first of which will be a smartphone due out before the end of the year. Tablets will follow at some point as well.
Lenovo on the other hand will actually be taking and tweaking Intel's own Medfield reference platform, and releasing it in China in Q2.
All of this is exactly what Intel needed: a start.
You can follow me on Twitter, add me to your circle on Google+ or or like my Facebook page to keep yourself updated on all the latest

0 comments:
Post a Comment